Ⅲ. JPA로 데이터베이스 다루기
개발 언어 : Java 8(JDK 1.8)
개발 환경 : Gradle 4.8 ~ Gradle 4.10.2
참조 :
기억보단 기록을
스프링 부트와 AWS로 혼자 구현하는 웹서비스 (프리렉, 이동욱 지음)
예제 코드 내려받기
프로젝트에 Spring Data Jpa 적용하기
build.gradle에 의존성 등록
dependencies {
compile('org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web')
compile('org.projectlombok:lombok')
compile('org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-jpa') //1.
compile('com.h2database:h2') //2.
testCompile('org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test')
}
- spring-boot-starter-data-jpa
- 스프링 부트용 Spring Data Jpa 추상화 라이브러리
- 스프링 부트 버전에 맞춰 자동으로 JPA 관련 라이브러리들의 버전을 관리
- h2
- 인메모리 관계형 데이터베이스
- 별도의 설치가 필요 없이 프로젝트 의존성만으로 관리
- 메모리에서 실행되기 때문에 애플리케이션을 재시작할 때마다 초기화된다는 점을 이용하여 테스트 용도로 많이 사용
domain 패키지는 도메인을 담을 패키지 이다.
도메인이란 게시글, 댓글, 회원, 정산, 결제 등 소프트웨어에 대한 요구사항 혹은 문제 영역이라고 생각하면 된다.
xml에 쿼리를 담고, 클래스는 쿼리의 결과만 담던 일들이 모두 도메인 클래스라고 불리는 곳에서 해결된다.
도메인에 자세하게 알고 싶다면 DDD Start 클릭
domain 패키지에 posts 패키지와 Posts 클래스 생성
Posts 클래스 코드 작성
src/main/java/com/freehyun/book/springboot/domain/posts/Posts
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
@Getter //6.
@NoArgsConstructor //5.
@Entity //1.
public class Posts {
@Id //2.
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) //3.
private Long id;
@Column(length = 500, nullable = false) //4.
private String title;
@Column(columnDefinition = "TEXT", nullable = false)
private String content;
private String author;
@Builder //7.
public Posts(String title, String content, String author) {
this.title = title;
this.content = content;
this.author = author;
}
}
Posts 클래스는 실제 DB의 테이블과 매칭될 클래스이며 보통 Entity 클래스라고도 한다.
- @Entity
- 테이블과 링크될 클래스
- 기본값으로 클래스의 카멜케이스 이름을 언더스코어 네이밍(_)으로 테이블 이름을 매칭
- ex)SalesManager.java -> sales_manager table
- @Id
- 해당 테이블의 PK 필드를 나타낸다.
- @GeneratedValue
- PK 의 생성 규칙을 나타낸다.
- 스프링 부트 2.0 에서는 Generation Type.IDENTITY 옵션을 추가해야만 auto_increment 가 된다.
- @Column
- 테이블의 칼럼을 나타내며 굳이 선언하지 않더라도 해당 클래스의 필드는 모두 칼럼이 된다.
- 사용하는 이유는, 기본값 외에 추가로 변경이 필요한 옵션이 있으면 사용
- 문자열의 경우 VARCHAR(255) 가 기본값인데, 사이즈를 500으로 늘리고 싶거나(ex:title), 타입을 TEXT 로 변경하고 싶거나(ex: content) 등의 경우에 사용
- @NoArgsConstructor
- 기본 생성자 자동 추가
- public Posts() {}와 같은 효과
- @Getter
- 클래스 내 모든 필드의 Getter 메소드를 자동생성
- @Builder
- 해당 클래스의 빌더 패턴 클래스를 생성
- 생성자 상단에 선언 시 생성자에 포함된 필드만 빌더에 포함
Posts 클래스로 Database를 접근하게 해줄 JpaRepository 생성

src/main/java/com/freehyun/book/springboot/domain/posts/PostsRepository
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
public interface PostsRepository extends JpaRepository<Posts, Long> {
}
ibatis 나 MyBatis 등에서 Dao 라고 불리는 DB Layer 접근자, JPA 에선 Repository 라고 부르며 인터페이스로 생성
JpaRepository<Entity 클래스, PK 타입>를 상속하면 기본적인 CRUD 메소드가 자동으로 생성
@Repository 를 추가할 필요없다.
(주의) Entity 클래스와 기본 Entity Repository 는 함께 위치
Spring Data JPA 테스트 코드 작성하기
test 디렉토리 -> domain.posts 패키지 생성 -> PostsRepositoryTest 클래스 생성
PostsRepositoryTest 테스트 코드 작성
src/test/java/com/freehyun/book/springboot/domain/posts/PostsRepositoryTest
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import java.util.List;
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.assertThat;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class PostsRepositoryTest {
@Autowired
PostsRepository postsRepository;
@After //1.
public void cleanup() {
postsRepository.deleteAll();
}
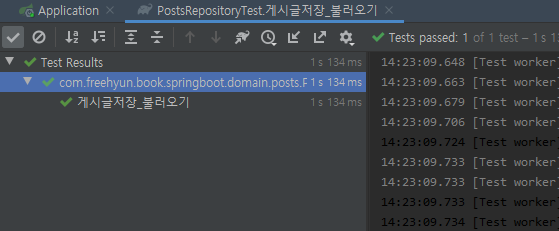
@Test
public void 게시글저장_불러오기() {
//given
String title = "테스트 게시글";
String content = "테스트 본문";
postsRepository.save(Posts.builder() //2.
.title(title)
.content(content)
.author("shounghyun@gmail.com")
.build());
//when
List<Posts> postsList = postsRepository.findAll(); //3. 테이블 posts 에 있는 모든 데이터를 조회해오는 메소드
//then
Posts posts = postsList.get(0);
assertThat(posts.getTitle()).isEqualTo(title);
assertThat(posts.getContent()).isEqualTo(content);
}
}
별다른 설정 없이 @SpringBootTest를 사용할 경우 H2 데이터베이스 를 자동으로 실행
- @After
- Junit 에서 단위 테스트가 끝날 때마다 수행되는 메소드를 지정
- 보통은 배포 전 전체 테스트를 수행할 때 테스트간 데이터 침범을 막기 위해 사용
- 여러 테스트가 동시에 수행되면 테스트용 데이터베이스인 H2에 데이터가 그대로 남아 있어 다음 테스트 실행 시 테스트가 실패할 수 있다.
- postsRepository.save
- 테이블 posts 에 insert/update 쿼리를 실행
- id 값이 있다면 update, 없다면 insert 쿼리가 실행
- postsRepository.findAll
- 테이블 posts 에 있는 모든 데이터를 조회해오는 메소드
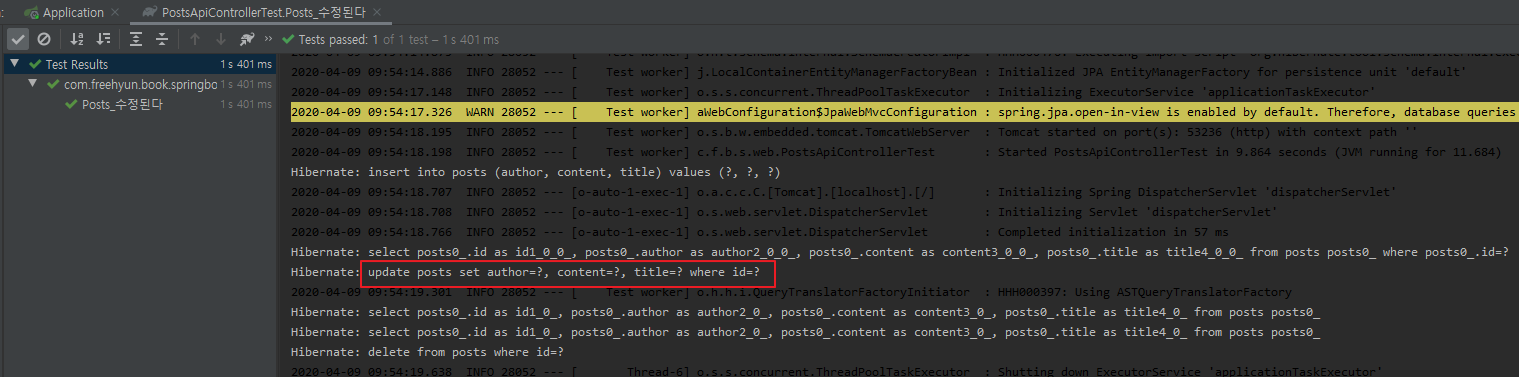
실행된 쿼리 로그보기
src/main/resources 디렉토리 아래에 application.properties 파일 생성
application.properties 옵션 추가
spring.jpa.show-sql=true
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect=org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5InnoDBDialect
옵션 추가되었다면 다시 테스트를 수행해서 쿼리 로그 확인
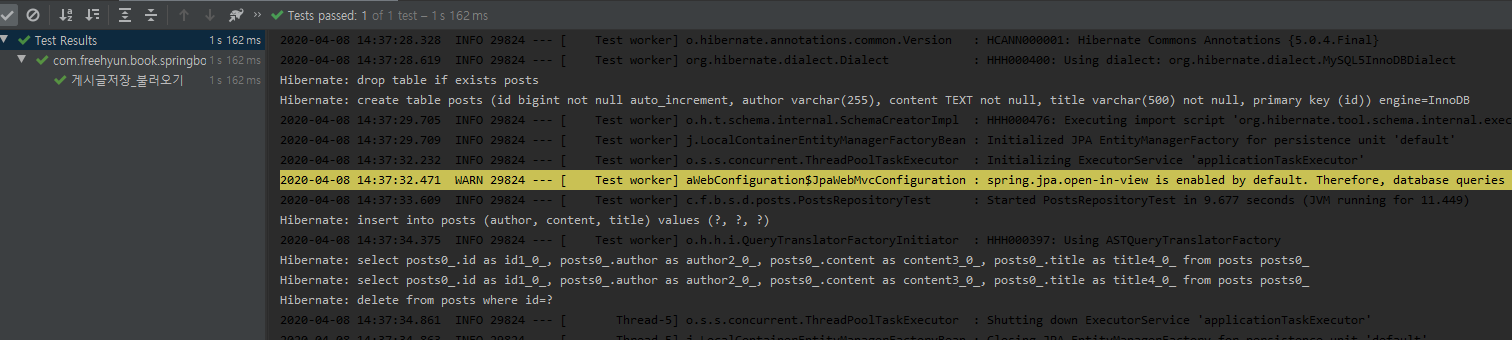
등록/수정/조회 API 만들기
PostsApiController를 web 패키지에, PostsSaveRequestDto를 web.dto 패키지에, PostsService를 service 패키지에 생성
PostsApiController
src/main/java/com/freehyun/book/springboot/web/PostsApiController
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@RestController
public class PostsApiController {
private final PostsService postsService;
@PostMapping("/api/v1/posts")
public Long save(@RequestBody PostsSaveRequestDto requestDto) {
return postsService.save(requestDto);
}
}
PostsService
src/main/java/com/freehyun/book/springboot/service/PostsService
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Service
public class PostsService {
private final PostsRepository postsRepository;
@Transactional
public Long save(PostsSaveRequestDto requestDto) {
return postsRepository.save(requestDto.toEntity()).getId();
}
}
PostsSaveRequestDto
src/main/java/com/freehyun/book/springboot/web/dto/PostsSaveRequestDto
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@Getter
@NoArgsConstructor
public class PostsSaveRequestDto {
private String title;
private String content;
private String author;
@Builder
public PostsSaveRequestDto(String title, String content, String author) {
this.title = title;
this.content = content;
this.author = author;
}
public Posts toEntity() {
return Posts.builder()
.title(title)
.content(content)
.author(author)
.build();
}
}
(주의) Entity 클래스를 Request/Response 클래스로 사용해서는 안된다. Entity 클래스는 데이터베이스와 맞닿은 핵심 클래스이다. Entity 클래스를 기준으로 테이블이 생성되고, 스키마가 변경된다.
꼭 Entity 클래스와 Controller에서 쓸 Dto는 분리해서 사용해야 한다.
test 패키지 중 web 패키지에 PostsApiControllerTest 생성
PostsApiControllerTest
src/test/java/com/freehyun/book/springboot/web/PostsApiControllerTest
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.boot.test.web.client.TestRestTemplate;
import org.springframework.boot.web.server.LocalServerPort;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import java.util.List;
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.assertThat;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
public class PostsApiControllerTest {
@LocalServerPort
private int port;
@Autowired
private TestRestTemplate restTemplate;
@Autowired
private PostsRepository postsRepository;
@After
public void tearDown() throws Exception {
postsRepository.deleteAll();
}
@Test
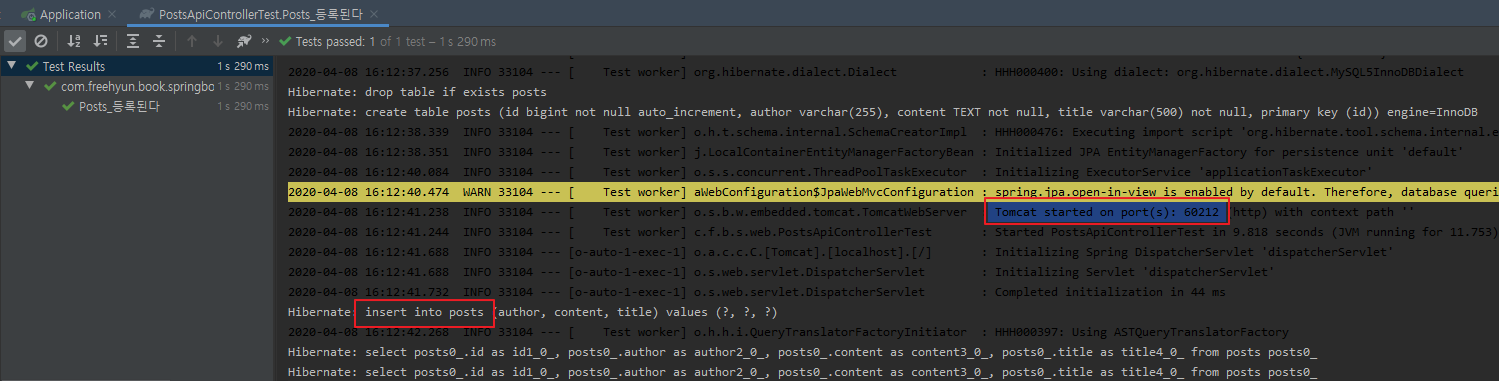
public void Posts_등록된다() throws Exception {
//given
String title = "title";
String content = "content";
PostsSaveRequestDto requestDto = PostsSaveRequestDto.builder()
.title(title)
.content(content)
.author("author")
.build();
String url = "http://localhost:" + port + "/api/v1/posts";
//when
ResponseEntity<Long> responseEntity = restTemplate.postForEntity(url, requestDto, Long.class);
//then
assertThat(responseEntity.getStatusCode()).isEqualTo(HttpStatus.OK);
assertThat(responseEntity.getBody()).isGreaterThan(0L);
List<Posts> all = postsRepository.findAll();
assertThat(all.get(0).getTitle()).isEqualTo(title);
assertThat(all.get(0).getContent()).isEqualTo(content);
}
}
@WebMvcTest의 경우 Controller와 ControllerAdvice 등 외부 연동과 관련된 부분만 활성화되고 JPA 기능이 작동하지 않는다. JPA 기능까지 한번에 테스트할 때는 @SpringBootTest와 TestRestTemplate을 사용하면 된다.
WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT로 인한 랜덤 포트 실행과 insert쿼리가 실행된 것 모두 확인했다.
수정/조회 기능 추가
PostsApiController
src/main/java/com/freehyun/book/springboot/web/PostsApiController
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@RestController
public class PostsApiController {
private final PostsService postsService;
...
@PutMapping("/api/v1/posts/{id}")
public Long update(@PathVariable Long id, @RequestBody PostsUpdateRequestDto requestDto) {
return postsService.update(id, requestDto);
}
@GetMapping("/api/v1/posts/{id}")
public PostsResponseDto findById (@PathVariable Long id) {
return postsService.findById(id);
}
}
PostsResponseDto
src/main/java/com/freehyun/book/springboot/web/dto/PostsResponseDto
import lombok.Getter;
@Getter
public class PostsResponseDto {
private Long id;
private String title;
private String content;
private String author;
public PostsResponseDto(Posts entity) {
this.id = entity.getId();
this.title = entity.getTitle();
this.content = entity.getContent();
this.author = entity.getAuthor();
}
}
PostsResponseDto는 Entity의 필드 중 일부만 사용 하므로 생성자로 Entity를 받아 필드에 값을 넣는다.
PostsUpdateRequestDto
src/main/java/com/freehyun/book/springboot/web/dto/PostsUpdateRequestDto
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@Getter
@NoArgsConstructor
public class PostsUpdateRequestDto {
private String title;
private String content;
@Builder
public PostsUpdateRequestDto(String title, String content) {
this.title = title;
this.content = content;
}
}
Posts
src/main/java/com/freehyun/book/springboot/domain/posts/Posts
public class Posts {
...
public void update(String title, String content) {
this.title = title;
this.content = content;
}
}
PostsService
src/main/java/com/freehyun/book/springboot/service/PostsService
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Service
public class PostsService {
...
@Transactional
public Long update(Long id, PostsUpdateRequestDto requestDto) {
Posts posts = postsRepository.findById(id).orElseThrow(() -> new IllegalArgumentException("해당 게시글이 없습니다. id="+ id));
posts.update(requestDto.getTitle(), requestDto.getContent());
return id;
}
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
public PostsResponseDto findById(Long id) {
Posts entity = postsRepository.findById(id).orElseThrow(() -> new IllegalArgumentException("해당 게시글이 없습니다. id="+ id));
return new PostsResponseDto(entity);
}
}
PostsApiControllerTest 수정기능 코드 추가
src/test/java/com/freehyun/book/springboot/web/PostsApiControllerTest
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
public class PostsApiControllerTest {
...
@Test
public void Posts_수정된다() throws Exception {
//given
Posts savedPosts = postsRepository.save(Posts.builder()
.title("title")
.content("content")
.author("author")
.build());
Long updateId = savedPosts.getId();
String expectedTitle = "title2";
String expectedContent = "content2";
PostsUpdateRequestDto requestDto = PostsUpdateRequestDto.builder()
.title(expectedTitle)
.content(expectedContent)
.build();
String url = "http://localhost:" + port +"/api/v1/posts/" + updateId;
HttpEntity<PostsUpdateRequestDto> requestEntity = new HttpEntity<>(requestDto);
//when
ResponseEntity<Long> responseEntity = restTemplate.exchange(url, HttpMethod.PUT, requestEntity, Long.class);
//then
assertThat(responseEntity.getStatusCode()).isEqualTo(HttpStatus.OK);
assertThat(responseEntity.getBody()).isGreaterThan(0L);
List<Posts> all = postsRepository.findAll();
assertThat(all.get(0).getTitle()).isEqualTo(expectedTitle);
assertThat(all.get(0).getContent()).isEqualTo(expectedContent);
}
}
조회기능은 실제로 톰캣을 실행해서 확인
로컬 환경에서 데이터베이스 H2를 사용
메모리에서 실행하기 때문에 직접 접근하려면 웹 콘솔을 사용
먼제 웹 콘솔 옵션을 활성화 한다. application.properties 옵션 추가
spring.h2.console.enabled=true
추가한 뒤 Application 클래스 main 메소드 실행
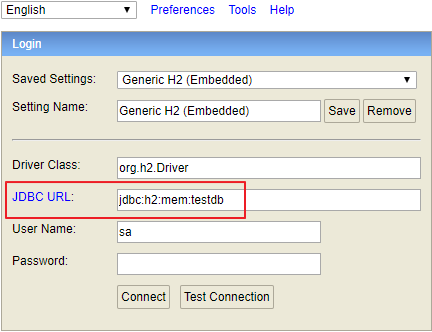
정상적으로 실행됐다면 톰캣이 8080포트로 실행된다. 웹브라우저에 http://localhost:8080/h2-console 로 접속하면 웹 콘솔 화면이 나온다. JDBC URL 에 jdbc:h2:mem:testdb 로 작성한다.
[Connect]클릭해서 H2 를 관리할 수 있는 관리 페이지로 이동

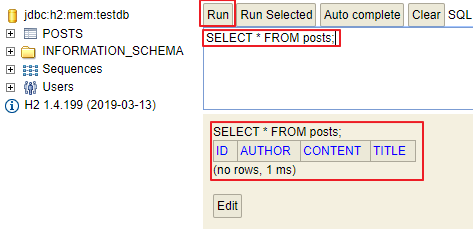
간단한 쿼리 실행
SELECT * FROM posts;
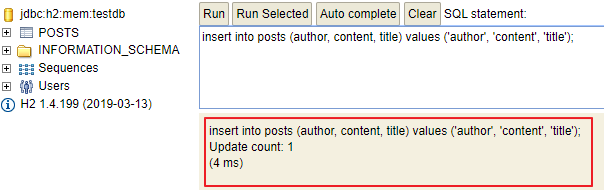
현재 등록된 데이터가 없기때문에 간단하게 insert 쿼리를 실행해보고 API로 조회해 보자
insert into posts (author, content, title) values ('author', 'content', 'title');
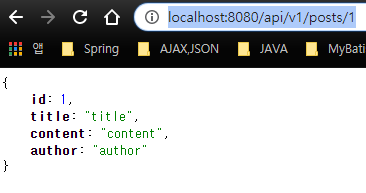
http://localhost:8080/api/v1/posts/1 을 입력해 API 조회 기능을 테스트 해보자
JPA Auditing으로 생성시간/수정시간 자동화하기
스프링 부트 1.x를 쓴다면 별도로 Hibernate 5.2.10 버전 이상을 사용하도록 설정이 필요하지만, 스프링 부트 2.x 버전을 사용하면 기본적으로 해당 버전을 사용 중이라 별다른 설정 없이 바로 적용.
domain 패키지에 BaseTimeEntity 클래스 생성
BaseTimeEntity 클래스 코드 작성
src/main/java/com/freehyun/book/springboot/domain/BaseTimeEntity
import lombok.Getter;
import org.springframework.data.annotation.CreatedDate;
import org.springframework.data.annotation.LastModifiedDate;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.domain.support.AuditingEntityListener;
import javax.persistence.EntityListeners;
import javax.persistence.MappedSuperclass;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
@Getter
@MappedSuperclass //1.
@EntityListeners(AuditingEntityListener.class) //2.
public abstract class BaseTimeEntity {
@CreatedDate //3.
private LocalDateTime createDate;
@LastModifiedDate //4.
private LocalDateTime modifiedDate;
}
BaseTimeEntity클래스는 모든 Entity의 상위 클래스가 되어 Entity들의 createdDate, modifiedDate를 자동으로 관리하는 역할
- @MappedSuperclass
- JPA Entity 클래스들이 BaseTimeEntity 을 상속할 경우 필드들 (createdDate, modifiedDate)도 칼럼으로 인식
- @EntityListeners(AuditingEntityListener.class)
- BaseTimeEntity 클래스에 Auditing 기능을 포함
- @CreatedDate
- Entity 가 생성되어 저장될 때 시간이 자동 저장
- @LastModifiedDate
- 조회한 Entity 의 값을 변경할 때 시간이 자동 저장
Posts 클래스가 BaseTimeEntity를 상속받도록 변경
...
public class Posts extends BaseTimeEntity {
...
}
마지막으로 JPA Auditing 어노테이션들을 모두 활성화활 수 있도록 Application 클래스에 활성화 어노테이션 추가
@EnableJpaAuditing // JPA Auditing 활성화
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
JPA Auditing 테스트 코드 작성하기
PostsRepositoryTest 클래스에 테스트 메소드 추가
@Test
public void BaseTimeEntity_등록() {
//given
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.of(2019, 6, 4, 0, 0, 0);
postsRepository.save(Posts.builder()
.title("title")
.content("content")
.author("author")
.build());
//when
List<Posts> postsList = postsRepository.findAll();
//then
Posts posts = postsList.get(0);
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>> createDate="+posts.getCreateDate()+", modifiedDate="+posts.getModifiedDate());
assertThat(posts.getCreateDate()).isAfter(now);
assertThat(posts.getModifiedDate()).isAfter(now);
}
댓글남기기